Traumatic Hepatic artery Transection Reconstructed with Splenic Artery Transposition Graft
Article information
Abstract
Traumatic injury of the hepatic artery is not common. However, it is a critical and lethal injury because of a higher risk of complication. Several methods for reconstruction of the hepatic artery have been described, including interposition of venous and prosthetic grafts, and transposition of native arteries to the distal stump of the hepatic artery. We describe a case of transposition to reconstruct the hepatic artery using the splenic artery.
CASE
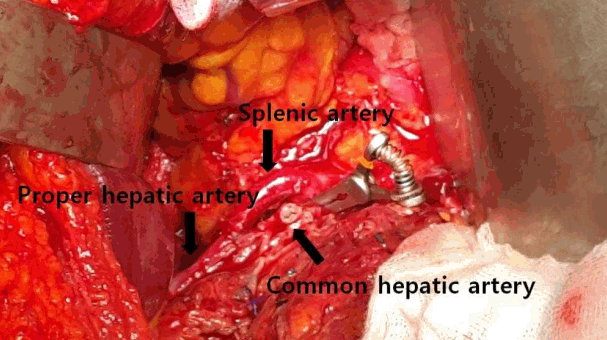
A 61-year-old male patient with a history of hypertension was admitted via the emergency room with blunt trauma. At admission, he was in shock status and had a positive focused abdominal sonography for trauma (FAST) sign. Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen-pelvis confirmed a hemoperitoneum and minor pancreatic injury (Fig. 1.). Therefore, emergency surgery was performed for the hemoperitoneum and detachment of the gastroduodenal artery from the common hepatic artery was found. Accordingly, the hepatic artery was reconstructed with a splenic artery transposition graft (Fig. 2.). After 10 days, a follow-up CT scan revealed normal perfusion status of the liver (Fig. 3.). The patient recovered and was discharged without complications.
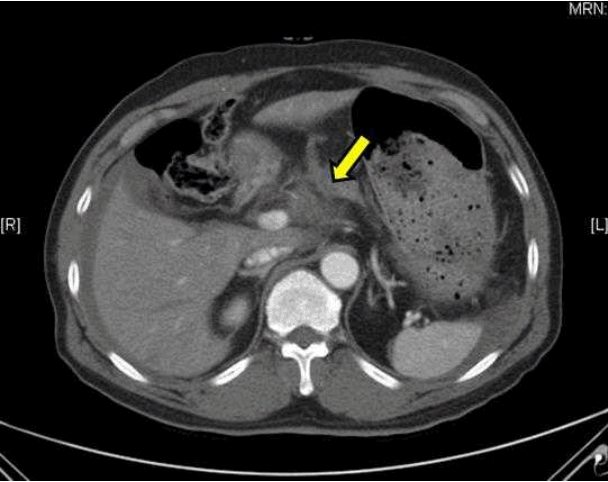
Abdominal CT shows ongoing bleeding of the common hepatic artery (yellow arrow) with hemoperitoneum.
DISCUSSION
Hepatic artery transection presents a technical challenge in vascular reconstruction. Various strategies to manage a hepatic artery injury have been described, ranging from ligation to complex vascular reconstruction [1]. Injuries to the hepatic arteries are uncommon in experienced hands [2]. In conclusion, splenic artery transposition is a simple and safe surgical option in patients with traumatic hepatic artery injury.
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.